HOBO Silicon Pyranometer Smart Sensor S-LIB-M003


The silicon pyranometer smart sensor is designed to work with HOBO® stations. The smart sensor has a plug-in modular connector that allows it to be added easily to a station. All calibration parameters are stored inside the smart sensor, which automatically communicates configuration information to the logger without any programming, calibration, or extensive user setup.
Accessories:
- Light sensor mounting bracket (M-LBB)
- Light sensor level (M-LLA)
Specifications
- Measurement Range 0 to 1280 W/m2
- Spectral Range 300 to 1100 nm (see Plot A)
- Accuracy Typically within ±10 W/m2 or ±5%, whichever is greater in sunlight; Additional temperature induced error ±0.38 W/m2/°C from 25°C (0.21 W/m2/°F from 77°F)
- Angular Accuracy Cosine corrected 0 to 80 degrees from vertical (see Plot B); Azimuth
- Error < ±2% error at 45 degrees from vertical, 360 degree rotation
- Resolution 1.25 W/m2
- Drift < ±2% per year
- Calibration Factory recalibration available
- Operating Temperature Range -40° to 75°C (-40° to 167°F)
- Environmental Rating Weatherproof
- Housing Anodized aluminum housing with acrylic diffuser and O-ring seal
- Dimensions 4.1 cm height x 3.2 cm diameter (1 5/8 in. x 1 1/4 in.)
- Weight 120 g (4 oz)
- Bits per Sample 10
- Number of Data Channels* 1
- Measurement Averaging Option Yes
- Cable Length Available 3.0 m (9.8 ft)
- Length of Smart Sensor Network Cable* 3.0 m (9.8 ft)
The CE Marking identifies this product as complying with all relevant directives in the European Union (EU). A single HOBO station can accommodate 15 data channels and up to 100 m (328 ft) of smart sensor cable (the digital communications portion of the sensor cables).
Spectral Characteristics
This sensor uses a silicon photodiode to measure solar power per unit area (watts per square meter). Silicon photodiodes are not ideal for use as solar radiation sensors and the photodiode in this silicon pyranometer is no exception (see Plot A). An ideal pyranometer has equal spectral response from 280 to 2800 nm. However, when calibrated properly and used correctly, the silicon pyranometer smart sensor should perform well in most situations.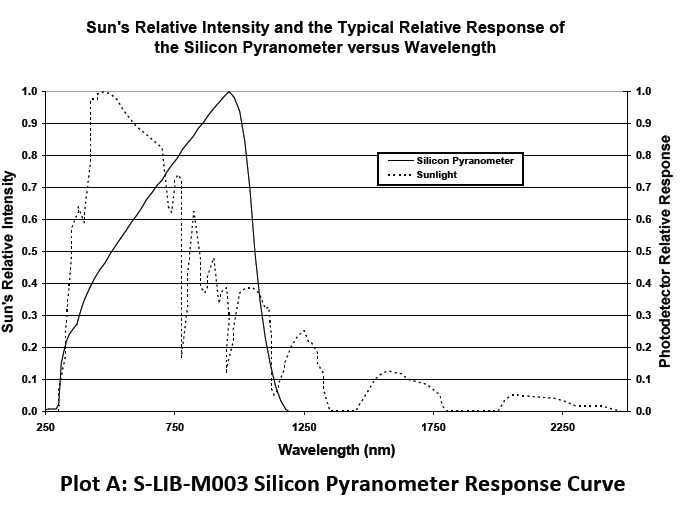

The sensor is calibrated for use in sunlight (an Eppley Precision Spectral Pyranometer is used as reference standard). Accordingly, if the sensor is used under natural sunlight, the measurement errors will be small. Note that significant errors may result from using the sensor under artificial light, within plant canopies, in greenhouses, or any other conditions where the spectral content differs from sunlight.
Cosine Correction
The silicon pyranometer smart sensor housing is designed to give an accurate cosine response. Plot B shows a plot of relative intensity versus angle of incidence for a typical sensor and for the theoretical ideal response. Deviation from ideal response is less than 5% from 0 to 70 degrees and less than 10% from 70 to 80 degrees. Note that as the angle approaches 90 degrees, the ideal cosine response approaches zero. As a result, small errors in measured intensity will result in very large percentage errors compared to the ideal response from 80 to 90 degrees.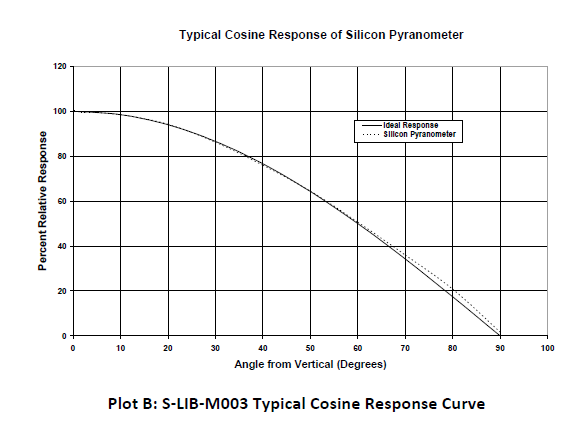

Mounting
Bracket Mounting
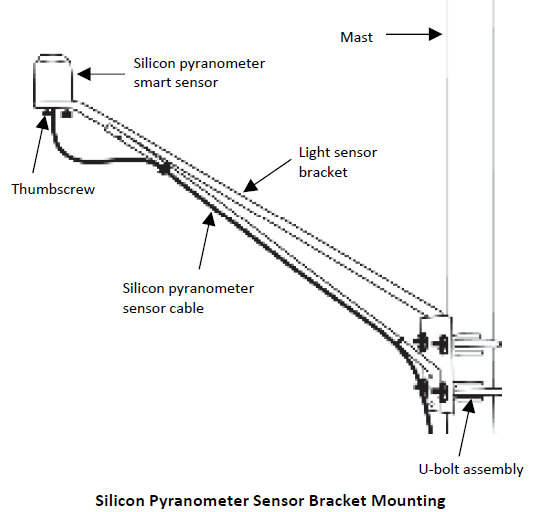
It is recommended that you mount the silicon pyranometer smart sensor with the light sensor bracket (M-LBB) on a pole or tripod. To mount the sensor using the bracket:
- Attach the light sensor bracket to a 1¼ inch – 15/8 inch pole with the provided U-bolts.Note: The bracket can also be mounted on a flat, vertical surface using four screws.
- Position the silicon pyranometer sensor on top of the bracket with its cable running through the slot in the bracket.
- Using the two screws supplied, attach the sensor to the bracket through the two holes on either side of the slot.Note: Do not completely tighten the screws until you level the sensor.
- Position the bracket so it faces toward the equator, minimizing the chance of shading.
- Mount the bracket on the mast with the two U-bolt assemblies, mounting it high enough on the mast to avoid the possibility of shading the sensor.Note: If you mount the sensor above eye level, it is recommended that you use a step ladder or other secure platform when leveling the sensor so that you can clearly view the light sensor level (M-LLA).

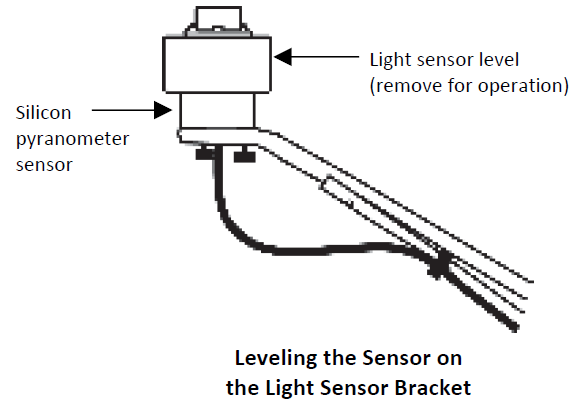
- Make sure the screws holding the sensor to the mounting bracket are loose.
- Place the light sensor level on the silicon pyranometer smart sensor.
- Adjust the height of the thumbscrews to level the sensor (start with the thumbscrews protruding about 1/16 inch from the bracket).
- Once the sensor is near level, tighten the Phillips head screws.
- Check the level and repeat above steps if necessary.
- IMPORTANT: Don’t forget to remove the level when you are done with it.

Specialized Application Mounting
To mount the silicon pyranometer sensor using a mounting plate of your own design:
- Drill a 0.56 (9/16) inch hole in the middle of the plate, then drill two #25 holes 1.063 (1-1/16) inches apart on either side of the center hole. Cut a 0.31 (5/16) inch-wide slot in the mounting plate. See diagram on next page. The plate should be a thickness of 1/8 inch or less.
- Slide the sensor through the 0.31 (5/16) inch-wide slot.
- Attach the sensor using two 6-32 x 3/8 inch screws and lock washers (not included).
- Shim the sensor as necessary to level it.


Mounting Considerations
- Small errors in alignment can produce significant errors. Be certain that the sensor is mounted level.
- Mount the sensor where it will not be in a shadow. Any obstruction should be below the plane of the sensor head. If that is not possible, try to limit obstructions to below 5 degrees, where the effect will be minimal.
- If possible, avoid locating the sensors in dusty locations. Dust, pollen, and salt residue that collect on the top of the sensor can significantly degrade accuracy.
- Refer to the station manual and Tripod Setup Guide for more information regarding setting up stations.
Connecting the Smart Sensor to a Station
To connect the sensor to a station, stop the station from logging and insert the smart sensor’s modular jack into an available smart sensor port on the station. See the station manual for details on operating stations with smart sensors.
Operation
The silicon pyranometer smart sensor supports measurement averaging. When measurement averaging is enabled, data is sampled more frequently than it is logged. The multiple samples are then averaged together and the average value is stored as the data for the interval. For example, if the logging interval is set at 10 minutes and the sampling interval is set at 1 minute, each recorded data point will be the average of 10 measurements. Measurement averaging is useful for reducing noise in the data.It is recommended that you use measurement averaging whenever the silicon pyranometer smart sensor is placed in an area where the light level can vary quickly with respect to the logging interval (for example, during partly cloudy conditions).Note that fast sampling intervals less than 1 minute may significantly reduce battery life. See the station manual for more details about battery life.
Maintenance
Dust on the sensor will degrade sensor accuracy. Periodically inspect the sensor, and if necessary, gently clean the diffuser with a damp sponge. Do not open the sensor as there are no user serviceable parts inside.
Warning: DO NOT use alcohol, organic solvents, abrasives, or strong detergents to clean the diffuser element on the silicon pyranometer smart sensor. The acrylic material used in the sensors can be crazed by exposure to alcohol or organic solvents. Clean the sensor only with water and/or a mild detergent such as dishwashing soap if necessary. It is recommended that you use vinegar to remove hard water deposits from the diffuser element. Under no circumstances should the smart sensor be immersed in any liquid.
Verifying Sensor Accuracy
It is recommended that you test the silicon pyranometer smart sensor annually for accuracy. If the sensor is not providing accurate data, it may be damaged or out of calibration.
© 2001–2017 Onset Computer Corporation. All rights reserved. Onset and HOBO are trademarks or registered trademarks of Onset Computer Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective companies.


[xyz-ips snippet=”download-snippet”]


